P07-30
Application of Amino-Acid Mapping: Activity Prediction for Drug Discovery
Yuka MATSUMOTO *1, Akito SABURI1, Kyosuke TSUMURA2, Issei DOI2, Yasushi HIKIDA1
1Imaging & Informatics Laboratory, Fujifilm Corporation
2Analysis Technology Center, Fujifilm Corporation
( * E-mail: yuka.b.matsumoto@fujifilm.com )
In drug discovery, in silico technologies have been widely used to calculate the interactions between compounds and proteins based on their chemical structures, and furthermore, to predict the biological activities of compounds. We have developed Amino-Acid Mapping (AAM) descriptor which can characterize the interactions between compounds and nearby amino acid residues, and demonstrated that the similarities of AAM profiles to those of a known active compound corresponds to the binding energies calculated based on FMO method and their pIC50 values towards protein tyrosine kinase SYK inhibitor [1-3].
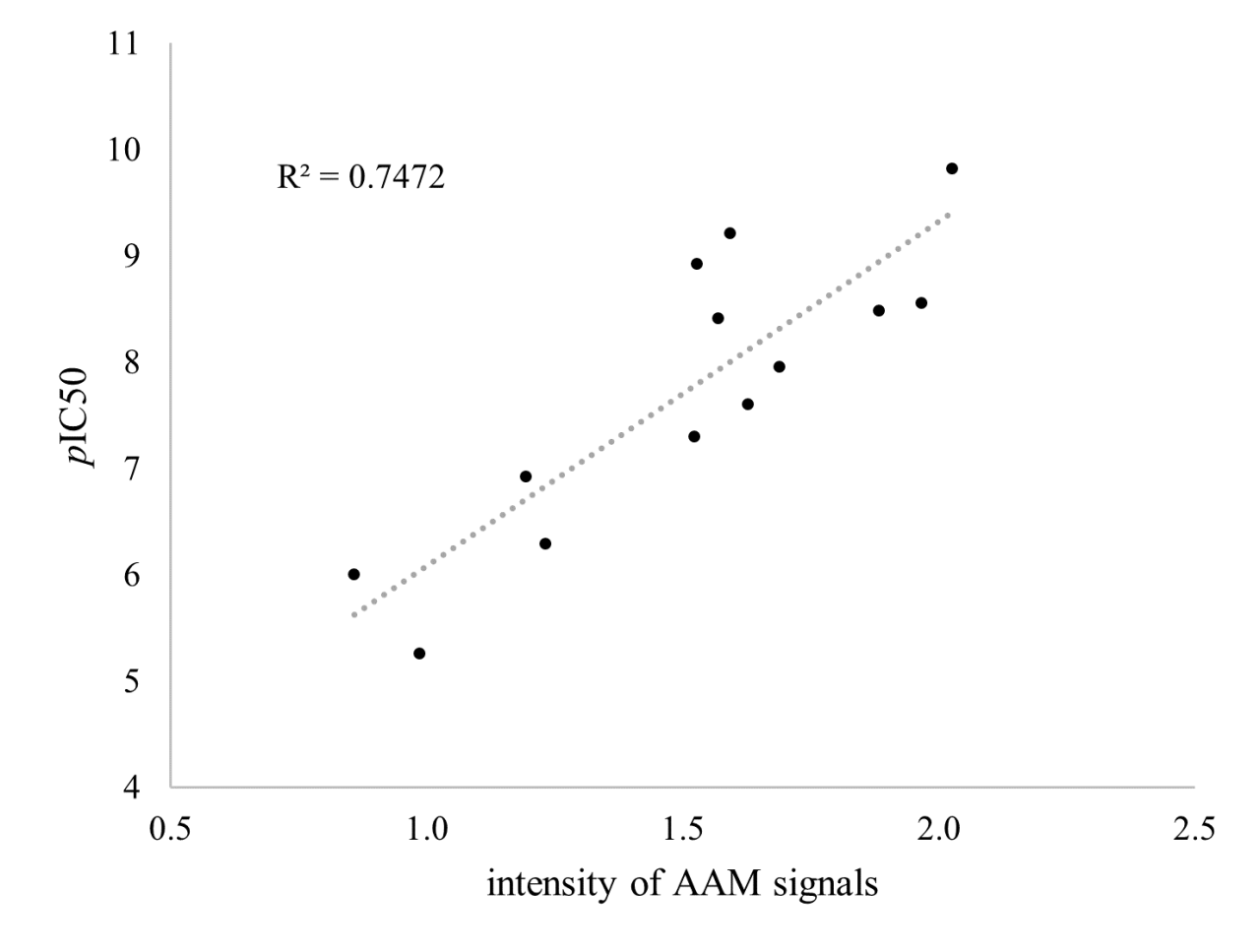
Herein, we report that the intensities AAM signals themselves would inherently contain information about the biological activities of compounds. Regarding the inhibitory activities towards SYK, we confirmed that compounds with higher intensities of AAM tend to have higher pIC50 values. Although the overall intensities AAM signals showed a weak correlation with pIC50 value, the intensities of AAM signals partitioned by atomic groups of the compounds exhibited a good correlation with pIC50 value (Fig.).
Furthermore, the strength of the correlation between the intensities of AAM signals and pIC50 values varied depending on the type of amino acids. Among them, the intensities of AAM signals of Asp, which makes a key interaction between SYK, were included in the group with a strong correlation with pIC50 values. This result indicated that AAM descriptor can provide insights into chemical motifs of the ligands and the amino acid residues, which are involved in the binding, without any structural information of the target protein.
Therefore, the AAM descriptor can be used not only to improve the similarity with biologically active compounds but also to predict their biological activities. It was also demonstrated that our AAM methodology has the potential to discovery and design high activity compounds based on the structural information. As another application, the correlation between the intensities of AAM signals partitioned by atomic groups and pIC50 values can be applied to provide structural insights related to the biological activities.
[1]Mao Tanabe et al., bioRxiv (2023), doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.03.547598
[2]Fujifilm started a CRO service based on AI-AAM, i.e., drug2drugs®. See the following URL for a detailed description: https://labchem-wako.fujifilm.com/jp/custom_service/products/95323.html
[3]Jun Nakabayashi et al., CBI Annual Meeting 2023, P03-07.