P07-01
Development of Pre-Fragment-Based MMP Analysis
Toshiaki WATANABE *, Osamu IWAMOTO, Hiroyuki HAKAMATA
R&D Division, DAIICHI SANKYO CO., LTD.
( * E-mail: toshiaki.watanabe@daiichisankyo.com )
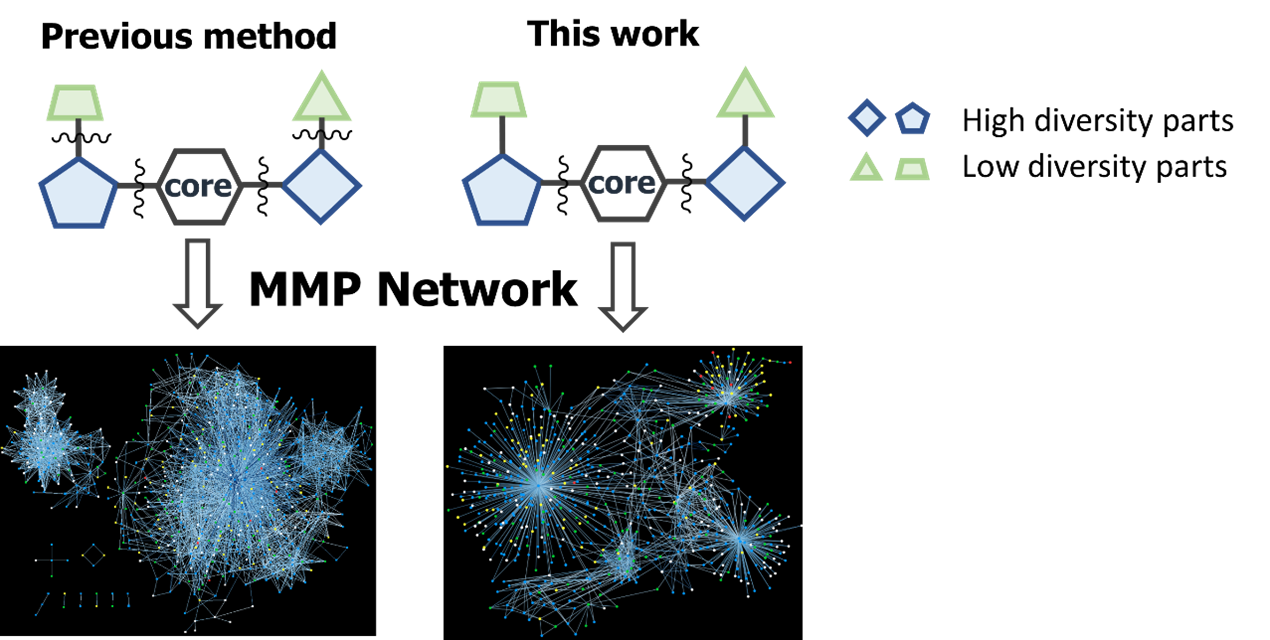
Matched Molecular Pairs (MMPs) are defined as pairs of compounds that differ at only one specific point in their molecular structure.1,2 Structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis can be performed by examining the differences in pharmacological activity and ADMET properties associated with the structural changes between these compound pairs. However, MMPs are typically generated by fragmenting molecules according to uniform rules, which may also cleave less frequently transformed (less diverse) moieties. This often results in the generation of a large number of MMPs, which complicates the post-processing steps required to extract meaningful insights. To address this issue, we propose a method that enables more efficient SAR analysis by allowing cleavage at arbitrary positions based on synthetic synthons. This approach improves the relevance and manageability of the generated MMPs.
To demonstrate the applicability of our method, we conducted two case studies: (1) application to patent analysis and (2) application to modalities other than small molecules. In these drug discovery projects, our approach facilitated more efficient SAR analysis, improved patent key compound prediction, and enabled SAR visualization of medium-sized molecules.
1. Ed Griffen, Andrew G. Leach, Graeme R. Robb, and Daniel J. Warner. Matched Molecular Pairs as a Medicinal Chemistry Tool, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 22, 7739-7750
2. Mathias Wawer and Jürgen Bajorath. Local Structural Changes, Global Data Views: Graphical Substructure−Activity Relationship Trailing. J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 8, 2944-2951