P06-01
Cell State Analysis of Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment with Deep Learning
Jiaxin LI* 1, Artem LYSENKO 2, 3 , Tatsuhiko TSUNODA 2, 3
1 Department of Computational Biology and Medical Sciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo
3 RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Science
( * E-mail: 1530221035@edu.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp )
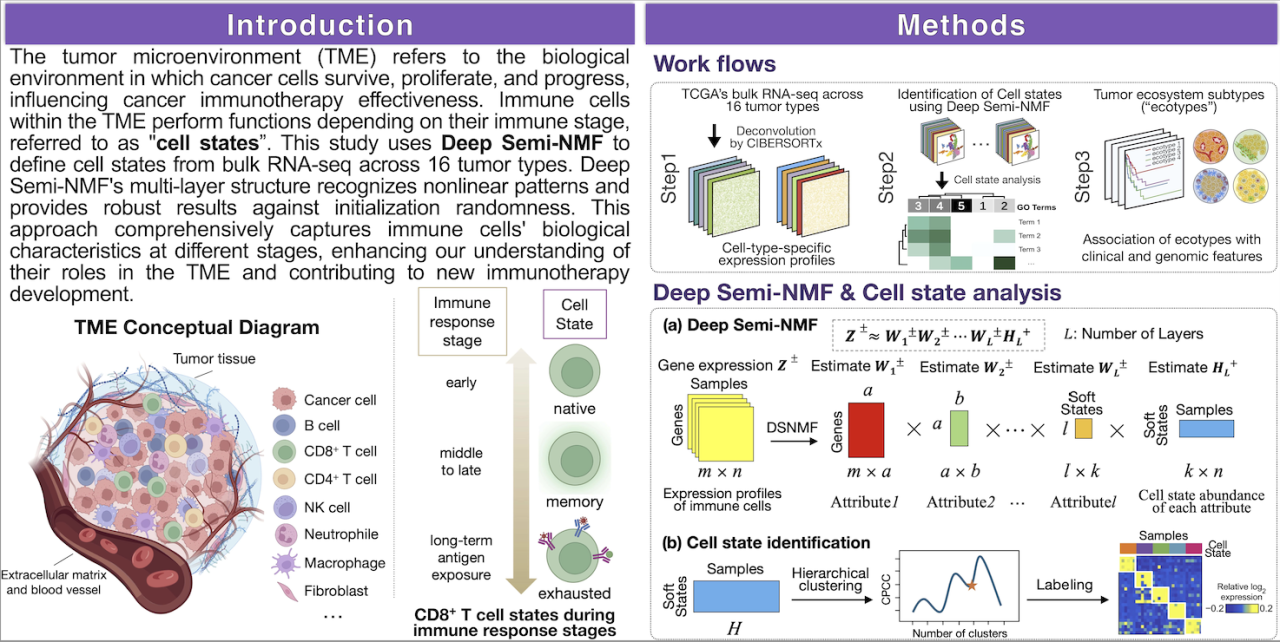
Immunotherapy is a revolutionary advancement in cancer treatment, targeting the body's immune system to fight malignancies more effectively. However, its success varies among patients due to the complexity of the tumor microenvironment.
EcoTyper, a machine learning tool, uses gene expression data to identify distinct immune cell states, offering insights into the tumor's immunological landscape. This study enhances EcoTyper with Deep Semi-NMF, refining cellular process analysis by extracting features at multiple hierarchical levels. This method is effective for complex cancer datasets, like those from 6000 patients across 16 cell types in TCGA. Deep Semi-NMF’s layered approach abstracts general cellular characteristics in the first layer, then delves into specific immune cell interactions in subsequent layers. This allows for more nuanced identification of cell states, improving immune response classification. More immune cell states are identified compared to traditional NMF techniques. Each new cell state is correlated with specific clinical outcomes, linking molecular insights to therapeutic impacts. This is crucial for understanding how different immune states affect immunotherapy efficacy, providing pathways to enhance patient response rates.
The insights from the Deep Semi-NMF enhanced EcoTyper model extend into areas of immune evasion and personalized treatment strategies. By understanding how certain immune cell states correspond to patient susceptibility or resistance to immunotherapy, clinicians can tailor treatments to leverage the immune system more effectively, offering hope for improved survival rates and quality of life for patients.