P05-04
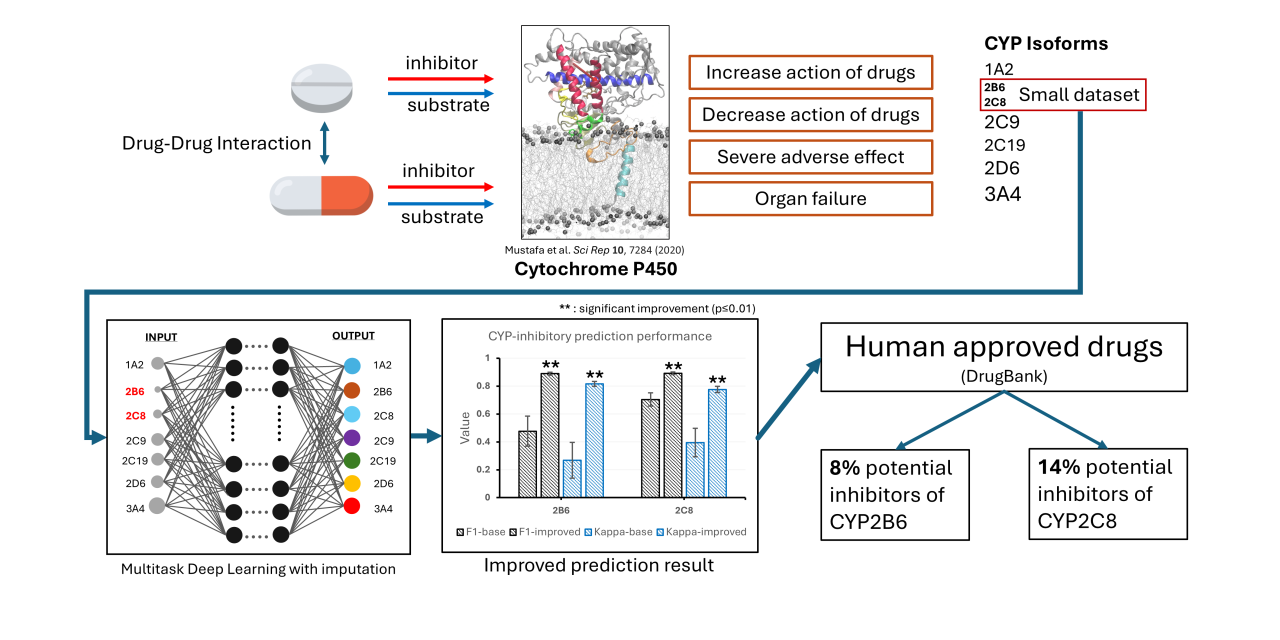
Improving the performance of prediction models for small datasets of cytochrome P450 inhibition with deep learning
ELPRI EKA PERMADI *1, 2, Reiko WATANABE1, Kenji MIZUGUCHI1
1Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, Japan
2Research Center for Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Traditional Medicine, National Research and Innovation Agency, Indonesia
( * E-mail: elpri@protein.osaka-u.ac.jp )
The human cytochrome P450 (CYP) is the major enzyme that metabolizes drugs, xenobiotics, and toxins. It is known that drug-drug interactions and drug-induced CYP inhibition can lead to adverse events. Thus, identifying potential CYP inhibitors is crucial for safe drug administration, especially for the least known CYP isoforms. However, CYP2B6 and CYP2C8 are currently more difficult to collect sufficient amounts of data than the five major CYPs, i.e., CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4/5, and it made difficult to build a predictive model with sufficient accuracy. This study aims to develop and validate a deep learning model for predicting cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition by focusing on isoforms with limited data availability using related data from major CYP isoforms with larger data. Additionally, we explored the inhibitory activity of approved drugs against CYP enzymes based on the constructed prediction models for CYP inhibition. Initially, a comprehensive dataset of around 12 thousand data points targeting seven CYP isoforms was compiled from public databases. Then, we constructed single task, fine-tuning, and multitask models incorporating data imputation of predicted data. We highlighted the potential of multitask deep learning models with predicted data imputation, achieving significant improvement (p≤0.01) in CYP inhibition prediction compared to the single task model. In addition, three multitask models trained on data imputed with predictions were successfully applied to identify 8% and 14% of human-approved drugs that potentially inhibit CYP2B6 and CYP2C8, respectively. Utilizing multitask learning with imputation of the missing values is useful for improving the performance of the CYP small dataset. Furthermore, discovering the potential inhibitors of CYP2B6 and CYP2C8 may help the practician to prevent drug adverse events by avoiding the combination of drugs.