P03-26
Drug discovery study integrating compound generative AI and molecular docking
Noriaki OKIMOTO3, Makoto TAIJI3, Mariko OKADA1
1Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University
2WPI-PRIMe, Osaka University
3Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, RIKEN
( * E-mail: okimoto@riken.jp )
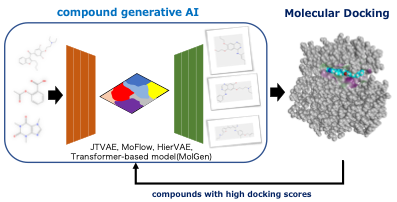
In recent years, AI for compound generation has gained significant attention as a crucial technology in drug discovery. This study aims to advance drug discovery by integrating AI-driven compound generation with molecular docking. The AI-driven system combines VAE, Flow, and GPT models to generate potential inhibitors targeting specific proteins, and its drug discovery capabilities are evaluated to assess its effectiveness in discovering novel compounds.
In this research, we focused on discovering inhibitors targeting thymidine phosphorylase (TP). TP is an enzyme involved in the catabolism of thymidine and is an important factor in promoting cellular aging, as well as serving as a target for cancer suppression. Additionally, several TP inhibitors have been identified. Using this drug discovery system, we generated compounds with high docking scores, selected those with high structural similarity from a commercial chemical library, and performed experimental evaluations. These evaluations revealed that several compounds successfully demonstrated TP inhibitory activity. We are currently optimizing these active compounds and continuing validation in close collaboration with experimental studies. We will provide the details on the day.