P03-22
Astellas's Digital Transformation for Small Molecule Drug Discovery Research
Takanobu ARAKI *1, Ikumi KURIWAKI1, Wataru HAMAGUCHI1, Toshiyuki OHFUSA2, Kazuya NAGAOKA2, Arina AFANASEVA2, Natnael HAMDA2, Kenichi MORI2, Kenji NEGORO1
1Platform Sciences & Modalities, Discovery Intelligence, Applied Research & Operations, Astellas Pharma Inc.
2Modality Informatics ResearchX, DigitalX, Astellas Pharma Inc.
( * E-mail: takanobu.araki@astellas.com )
Recent years have seen remarkable progress in digital technologies such as AI, simulation, and robotics across various industries. These technologies are utilized to drive digital transformation efforts with the goal of revolutionizing business operations and generating new value. The situation for pharmaceuticals reflects that in other industries. Digital technologies are expected to improve productivity in the drug discovery research process, allowing pharmaceutical companies to deliver better drugs to patients as quickly as possible.
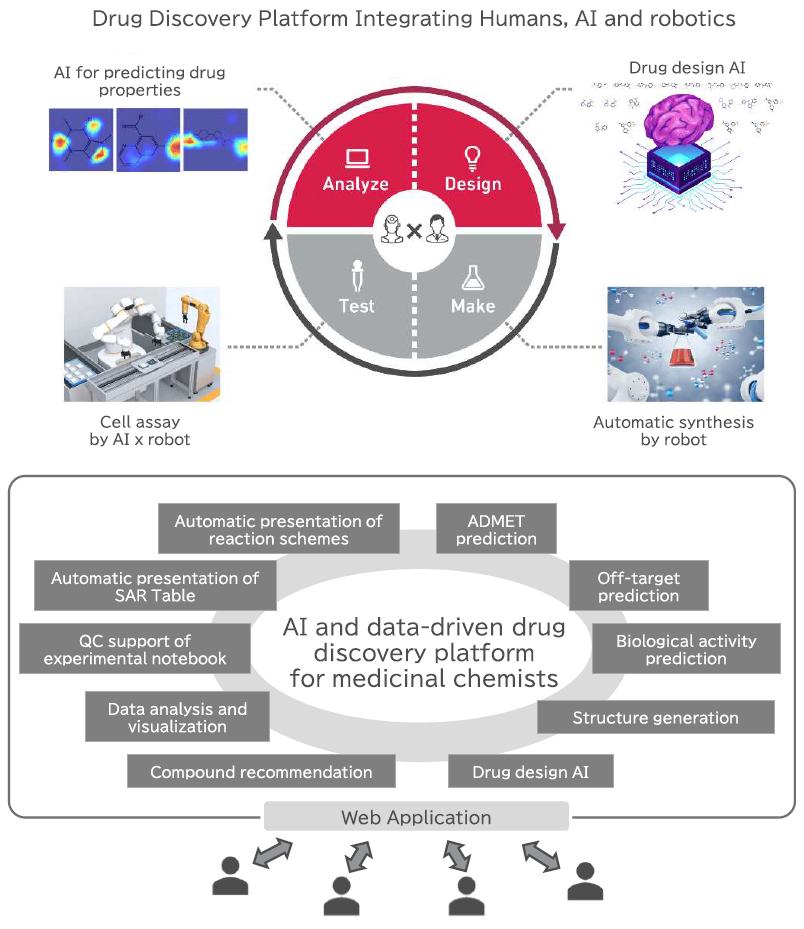
The optimization process, which accounts for the majority of small-molecule drug discovery research, is called the Design-Make-Test-Analysis (DMTA) cycle. Researchers iterate this cycle, while integrating feedback from experiment results into the process, to refine their hit compounds into clinical candidates. As part of our digital transformation efforts to accelerate drug optimization research, we have installed AI/robot technologies such as ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity) and activity predictions, chemical structure generation and robot synthesis into each step of the DMTA cycle (Figure 1). This collaborative system between humans and AI/robots has enabled us to create high-quality drug candidates in a shorter period of time, successfully achieving an approximately 70% reduction in the time from a hit compound to a clinical candidate.
To further improve the system we developed, it is important to expand the user base and develop talent. The Dx tools on the platform were developed by medicinal chemists using the low-code/no-code platform KNIME®. The user-friendly tools were well received by other medicinal chemists, resulting in more users. Some users even expressed interest in creating their own tools. In response, KNIME® workshops were held to train medicinal chemists to become tool developers as well as to improve their data handling and analysis skills. These efforts induced the trainees to generate new ideas for improving operational processes. The tools developed in collaboration with them enhanced the efficiency of research operations.
In this poster presentation, we will introduce an overview of our drug discovery platform which integrates humans, AI and robotics, and tools that enhance the productivity of medicinal chemists.