O06_02
Comparison Between Word Embeddings and Molecular Descriptors by Clustering and Distribution Analysis from Antioxidant Articles
Yuto MATSUMOTO *, Hiroaki GOTOH
Graduate School of Engineering, Yokohama National University
( * E-mail: matsumoto-yuuto-sh@ynu.jp)
In chemistry, antioxidant, which protect oxidation to organism, such as cell wall, is very important factor in the view of immunity. However, antioxidant effect is emerged by various mechanisms and various reaction, so exploration of antioxidant is very difficult without many trials or filtering. On the other hand, the large amount of previous study about antioxidant was published but only parts of those are used by each chemist. Focusing on this untouched information to predict antioxidant capacity and seek important factor of prediction or emerging mechanisms, we process antioxidant journals by natural language processing(NLP).
For examples of NLP in chemistry, there are ChemDataExtractor and few-shot learning using generative pre-trained transformer models. On the other hand, most of the currently reported models focus on information extraction and qualitative prediction, and there are few examples in which NLP models are combined with molecular descriptors, which are quantitative values calculated from the structure of compounds, and using to predict. so our purpose sets quantitative prediction, we compared between descriptors and embeddings, and investigated projection between those in this study.
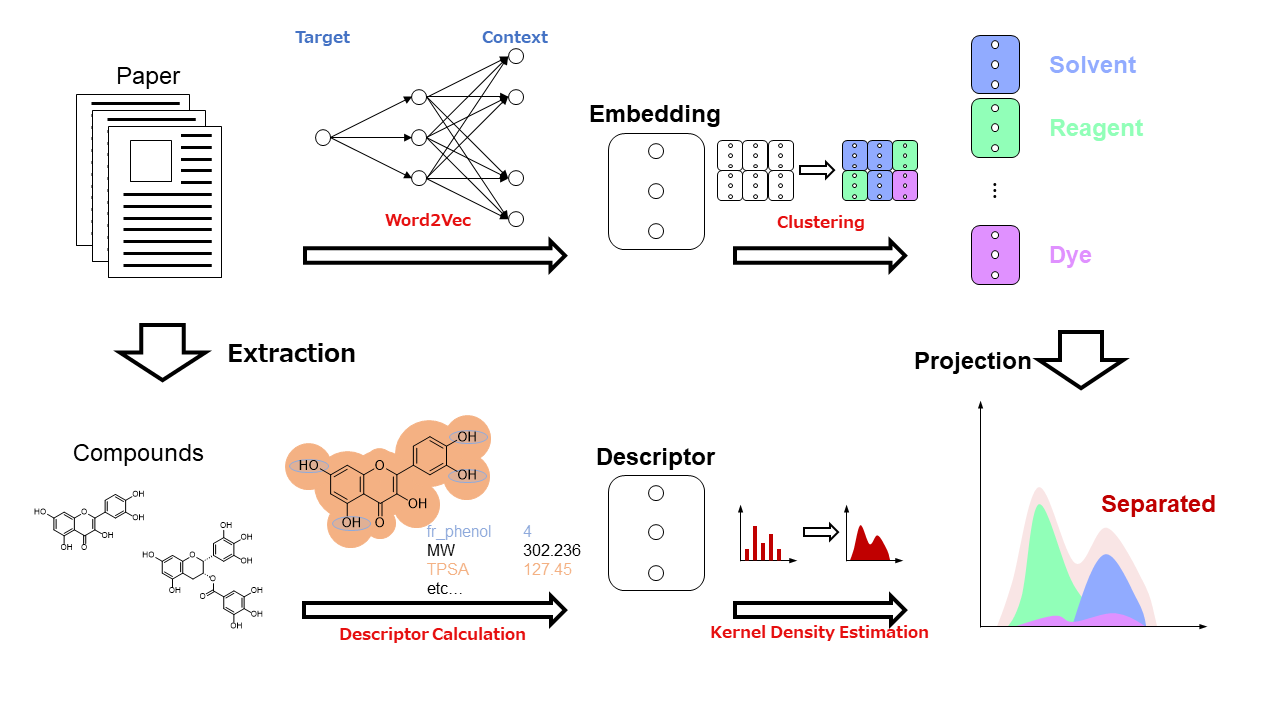
We obtained 1744 articles of Antioxidants, which is the journal published by MDPI corporation, from 1996 to 2020 and used the Word2Vec model to obtain embeddings. Among the embeddings, 1294 words meaning compounds were clustered. In the compounds classified by the clustering, we identified features in the usage of each cluster, such as being used as a solvent, a reagent, involved in the mechanism of action in the body, and used as a target for antioxidant capacity assays. In addition, we identified structural features of the compounds, such as the abundance of flavonoids, in some clusters. To analyze in detail the correlation of this classification on structural features, kernel density estimation (KDE) was performed on 208 standardized molecular descriptors, which has calculated by RDKit, over each cluster. This confirmed the distribution of molecular descriptors by cluster based on the mean, variance, and graph shape of the KDEs. In this visualization, clusters often had isolated means or low variances, and simple modal curve even though we did not use molecular descriptors under clustering methods. The results confirm the dependence of each cluster on molecular descriptors. Two of the clusters tended to have a specific shape with respect to the classified compounds and their molecular structures. This study revealed that there is a correspondence between linguistic analysis using embeddings and the meaning of structures in the compound space represented by molecular descriptors. We plan to use this method to clarify the structural effects on activity from the results of linguistic processing of various journals.